Materi tentang kalor merupakan salah satu materi penting untuk dipelajari karena cukup sering keluar dalam ujian semester maupun ujian nasional. Pada bagian akhir akan diberikan contoh soal kalor dan pembahasannya. Contoh soal kalor yang diberikan berupa contoh soal grafik perubahan wujud zat.
Ada beberapa rumus kalor yang digunakan untuk menentukan berapa banyak kalor yang dilepaskan pada saat benda mengalami perubahan wujud zat. Penggunaan rumus kalor tersebut tergantung dari keadaan yang dialami suatu zat. Apakah mencair, menguap, atau keadaan lainnya.
Bagaimana penggunaan rumus kalor untuk menentukan kalor yang dilepaskan suatu zat? Simak ulasan materi tentang kalor dan cara menetukan kalor yang dilepaskan pada contoh soal grafik perubahan wujud melalui halaman ini.
Simak ulasan video di bawah ini yah !

Materi pertama yang akan disampaikan adalah pengertian kalor dan rumus kalor. Simak ulasannya pada materi di bawah.
Pengertian Kalor, Satuan Kalor, dan Rumus Kalor
Kalor adalah bentuk energi yang dapat berpindah dari suatu tempat ke tempat lain karena perbedaan suhu. Dalam pembelajaran, kalian akan diminta untuk menentukan banyaknya kalor yang diterima atau kalor yang dilepaskan suatu zat. Dalam perubahan zat, kalor sendiri dibagi menjadi 2 (dua) jenis yaitu kalor untuk menaikkan suhu dan kalor laten.
Pada kalor untuk menaikkan suhu, besarnya kalor yang dihitung adalah kalor saat terjadinya perubahan (kenaikan) suhu. Sedangkan pada kalor laten, kalor yang dibutuhkan pada perubahan wujud zat. Kalor laten dibedakan menjadi dua yaitu kalor lebur dan kalor uap.
Kalor lebur dilepaskan saat terjadinya perubahan zat dari padat menjadi cair (mencair). Sedangkan kalor uap dilepaskan saat terjadinya perubahan zat dari cair menjadi uap (menguap).
Satuan Kalor dinyatakan dalam Joule (J) atau Kalori (kal), dengan hubungan yang dinyatakan sebagai berikut.
Satuan kalor:
Satuan kalor dinyatakan dalam Joule (J) atau kalori (kal). Hubungan antara keduanya dinyatakan melalui persamaan di bawah.
1 J = 0,24 kal
1 kal = 4,2 J
Sekarang, simak rumus kalor untuk menaikkan suhu yang akan diberikan di bawah.
Rumus kalor untuk menaikkan suhu:
alt="\[Q = m \cdot c \Delta T \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e1aa9cf92005022a0815f800d518cf68_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:83px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[Q = C \cdot \Delta T \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3edc91d67fb6c44596ba100024dca61d_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:76px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
Keterangan:
Q = kalor alt="(J)" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7c5e030e2a9402c33e5f449aa251ea50_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:19px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
m = massa alt="(kg)" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c676c942d38784d2c0092f484ce34a5f_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:25px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
c = kalor jenis alt="(J/kg^{o}C)" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8a3b18eca71150299e9df0a0d0b30f06_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:59px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
C = kapasitas kalor alt="(J/^{o}C)" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d6ec03e8a90249d33cdc9eb514293206_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:43px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\Delta T" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f083a74dc5d78c0a1258345a614242b0_l3.svg" style="height:11px; width:23px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" /> = perubahan suhu alt="(^{o}C)" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b938c96531b35b0afbcfbbae376e998e_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:27px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
Selanjutnya, simak juga rumus kalor laten yang terdiri atas kalor lebur dan kalor uap.
Keterangan:
Q = kalor alt="(J)" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7c5e030e2a9402c33e5f449aa251ea50_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:19px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
m = massa alt="(kg)" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c676c942d38784d2c0092f484ce34a5f_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:25px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
U = kalor uap alt="(J/kg)" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-088118f774d5136e3749197ea61177a1_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:41px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
L = kalor lebur alt="(J/kg)" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-088118f774d5136e3749197ea61177a1_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:41px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
-
Rumus kalor untuk mengubah wujud (Kalor Laten):
-
Kalor Uap: Cair ke Gas (menguap)
alt="\[Q = m \cdot U \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-80747293998db1c9dbd73c3e2384bcac_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:66px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
-
Kalor Lebur: Padat ke Cair (melebur/mencair)
alt="\[Q = m \cdot L \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-739fef6026bf28d4146f130ad54b156d_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:64px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
Sebelum mempelajari proses menghitung kalor yang diterima atau dilepaskan sebuah benda, kita akan mengulas sedikit tentang satu asas dalam pembahasan kalor yang terkenal, yaitu asas black.
Asas Black:
Pada pencampuran dua benda yang berbeda suhunya maka benda yang suhunya tinggi akan melepaskan kalor. Kalor yang dilepaskan akan diserap oleh benda yang suhunya rendah sampai akhirnya suhu kedua benda sama. Secara singkat, Asas Black dinyatakan dalam persamaan berikut.
alt="\[Q_{lepas} = Q_{terima}\]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-035771a685c624d8be552d75de3e9790_l3.svg" style="height:15px; width:103px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
Catatan: Prinsip Asas Black hanya berlaku pada sistem terisolasi, artinya tidak ada pertukaran kalor dengan lingkungan.
Ulasan materi yang akan dibahas selanjutnya adalah menghitung nilai kalor yang dibutuhkan untuk suatu proses perubahan wujud zat.
Proses Mengitung Nilai Kalor
Perubahan wujud zat dari padat ke cari, atau cair ke gas membutuhkan kalor. Banyak kalor yang dibutuhkan unutk melakukan proses perubahan wujud zat tersebut dapat dihitung melalui sebuah rumus.
Pada bagian akhir akan diberikan contoh soal kalor dan pembahasannya. Contoh soal yang diberikan berupa contoh soal grafik perubahan wujud zat yang sudah dilengkapi dengan pembahasa. Jadi, simak sampai selesai materinya, oke?
Proses perhitungan kalor yang dilepaskan suatu zat biasanya digambarkan dalam sebuah grafik perubahan wujud zat. Penyampaian materi yang akan diberikan di sini berupa analisis grafik tersebut. Materi yang akan diberikan di sini berupa sebuah study kasus.
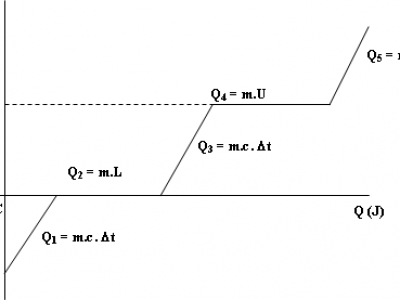
Perhatikan grafik proses perubahan wujud zat cair (dalam kasus ini air) pada gambar di bawah!
alt="rumus kalor" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/Grafik-Kalor-1-300x208.png" style="height:208px; width:300px" />
Proses dan besarnya kalor yang dibutuhkan dapat dilihat pada persamaan di bawah.
alt="\[Q_{1} = m_{es} \cdot c_{es} \cdot \left( T_{B} - T_{A} \right) \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2c456229b82d69282eefc06603d5192f_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:163px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[Q_{2} = m_{es} \cdot L \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f4f42916daa02ce7126ede8bdb928bf2_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:82px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[Q_{3} = m_{air} \cdot c_{air} \cdot \left( T_{C} - T_{D} \right) \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-aabd913b38d3b2aca9a708f03bc773fb_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:175px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[Q_{4} = m_{air} \cdot U \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7295667fb19674ca6e63e008a5bef110_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:88px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[Q_{5} = m_{uap} \cdot c_{uap} \cdot \left( T_{F} - T_{E} \right) \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-686ae1913888ccf87cb6fc0ce21bb84f_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:179px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[Q_{total} = Q_{1} + Q_{2} + Q_{3} + Q_{4} + Q_{5} \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7647f37c3a813d207aea036a00754de2_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:214px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
Contoh Soal dan Pembahasan
Contoh Soal Grafik Perubahan Wujud Zat (SOAL UN IPA FISIKA SMP 2016)
Perhatikan grafik pemanasan 1 kg es berikut ini!
alt="Contoh Soal Grafik Perubahan Wujud Zat" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/Grafik-Kalor-Soal--300x278.png" style="height:278px; width:300px" />
Jika kalor jenis es 2.100 J/kgoC, kalor lebur es 336.000 J/kg, dan kalor jenis air adalah 4.200 alt="J/kg^{o}C" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-fb0814114a8816d3ee29398784bc5d6a_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:49px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />maka kalor yang dibutuhkan dalam proses dari alt="P - Q - R" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e20653699eda2749894e823a6e4bc39f_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:69px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" /> adalah ….
A. 10.500 J
B. 21.000 J
C. 336.000 J
D. 346.500 J
Pembahasan:
Perhatikan gambar berikut untuk memduhakan menentukan rumus yang digunakan dalam menghitung setiap step proses kalor yang dilepaskan/dibutuhkan.
alt="contoh soal kalor dan pembahasannya" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/uploads/2017/08/Grafik-Kalor-Bahas-300x291.png" style="height:291px; width:300px" />
Kalor yang dibutuhkan untuk proses dari titik P ke Q adalah alt="Q_{1}" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4fbd8130ade9f93efa172befe6339f3a_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:16px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[ Q_{1} = m_{es} \cdot c_{es} \cdot \Delta T \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-3365fcc1e02db9ddc640ffdc661e0bf2_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:122px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[ Q_{1} = 1 \cdot 2.100 \cdot \left( 0 -(-5) \right) \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f25843661f117ed6919d2e015a1f6446_l3.svg" style="height:16px; width:165px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[ Q_{1} = 10.500 \; J \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d51087f6ef25d94f361fcd0e81fe6135_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:92px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
Kalor yang dibutuhkan untuk proses dari titik Q ke R adalah alt="Q_{2}" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e51f908be0060214616e75292ec91c96_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:17px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[ Q_{1} = m_{es} \cdot L \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e7fa5fe6388b81710cb2d379a0149cfe_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:82px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[ Q_{1} = 1 \cdot 336.000 \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-b5b560e0a3d3782aa6a88d352118a9dd_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:101px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[ Q_{1} = 336.000 \; J \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-91f85734239702e84f9ec65a4c0a109a_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:99px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
Kalor yang dibutuhkan untuk proses dari titik alt="P - Q - R" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e20653699eda2749894e823a6e4bc39f_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:69px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" /> adalah alt="Q_{1} + Q_{2}" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8778785f3765af433fcec9e56e07ce15_l3.svg" style="height:14px; width:53px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[ Q_{P - Q - R} = Q_{1} + Q_{2} \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5a968123e51ad9c75aa60845f16cfa05_l3.svg" style="height:15px; width:128px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[ Q_{P - Q - R} = 10.500 \; J + 336.000 \; J \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f1af2347f3fd5978bcb2a9e9c2e5e830_l3.svg" style="height:15px; width:208px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
alt="\[ Q_{P - Q - R} = 346.500 \; J \]" src="https://idschool.net/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-f32d72cea356caea49876b07c3fb7dd2_l3.svg" style="height:15px; width:137px" title="Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com" />
Jawaban: D
Sekian pembahasan mengenai materi kalor yang memuat pembahasan mengenai rumus kalor, contoh soal kalor dan pembahasannya, serta contoh soal grafik perubahan wujud zat.